
Take Our Free Journeyman Electrician Practice Test
100% Free Timed Journeyman Electrician Practice Exam!
No Credit Card or Trial Required.
Table of Contents
A Comprehensive Guide to the Journeyman Electrician Test
If you’re preparing to take the journeyman electrician exam, you’re in the right place. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know — from what’s on the test to how it’s scored, how it differs by state, and what you can do to prepare.
The journeyman electrician exam is a major milestone for electricians looking to work without supervision, increase their pay, or move toward a master license. While each state has its own licensing requirements, the exam itself is typically based on the National Electrical Code (NEC) and covers a mix of code lookups, calculations, and theory.
Whether you’re just starting to study or already deep into practice questions, this page will help you understand the process, avoid surprises, and take your next step toward becoming a licensed journeyman electrician.
What is the Journeyman Electrician Exam?
The journeyman electrician exam is a certification exam that proves you have the knowledge and experience to work independently on electrical systems while employed by a licensed contractor. It’s not a contractor license, but it’s the step that allows you to move beyond supervised work, and often have greater flexibility with moving between employers.
This exam is typically taken after completing a state-approved apprenticeship or accumulating several years of on-the-job experience. Passing it shows that you understand how to interpret the National Electrical Code (NEC), perform calculations, and follow proper safety practices.

Who Can Take the Journeyman Electrician Exam?
Before you can sit for the journeyman electrician exam, you’ll need to meet certain experience and education requirements. These vary by state, but most licensing boards expect you to have a combination of hands-on experience and classroom training.
Typical prerequisites include:
- At least 4 to 5 years of electrical work experience under a licensed contractor
- Completion of a registered apprenticeship program, or
- Complete a minimum of 250 hours of classroom instruction in electrical theory and code
If you’re unsure whether you qualify, check your state’s requirements here:
Journeyman Electrical License Requirements By State
How the Application Process Works
Once you meet the requirements, you’ll need to apply through your state’s licensing board. This usually involves submitting an application along with:
- Documentation of your work experience and training hours
- A government-issued photo ID
- Payment of an examination fee
Some states allow you to apply online, while others require you to mail in physical paperwork. Once approved, you’ll receive instructions on how to schedule your exam date.
What’s on the Journeyman Electrician Exam?

While every state creates its own version of the journeyman exam, the core content is the same nationwide — because nearly every state bases the exam on the National Electrical Code (NEC). The NEC is the foundation of the test, and it covers everything from wiring methods to load calculations to equipment installation rules.
In some states, you may also see a small number of questions covering electrical theory, safety standards, or basic troubleshooting concepts, but these typically make up a much smaller portion of the overall exam.
Below is a breakdown of the main topics you can expect to see, especially within the NEC portion — which accounts for the majority of your score.
National Electrical Code (NEC)
Most of the journeyman exam focuses on your ability to reference and apply the NEC. These questions are designed to test how well you can look up code sections quickly and apply the rules to real-world scenarios.
Here are the main NEC article groups you should be familiar with:
General – Articles 100 to 110
This section includes foundational information such as NEC definitions, equipment labeling, working space clearances, and general rules that apply across the entire code. You may see questions about:
- Article 100 definitions (like “grounded,” “bonded,” etc.)
- Working space around panels (clearance, lighting, etc.)
- Identifying hazardous locations and equipment markings
Wiring and Protection – Articles 200 to 250
This is one of the most heavily tested NEC sections. It covers the design and protection of electrical systems, and includes:
- Branch circuit and feeder requirements
- Load calculations for services and feeders
- Sizing and selecting overcurrent protection
- Rules for grounding and bonding of systems and equipment
- Underground and overhead service conductors
Wiring Methods and Materials – Articles 300 to 399
You’ll be tested on how wiring must be installed, supported, and protected. This section also covers materials and enclosures. Topics include:
- Installation requirements for raceways and cables
- Box fill calculations and conductor count
- Voltage drop calculations
- Pull box sizing
- Use cases and restrictions for different wiring methods (e.g., MC cable, flexible cords, etc.)
Equipment for General Use – Articles 400 to 490
This group covers everyday electrical equipment and how it’s installed. Expect questions about:
- Flexible cords and cable types
- Luminaires and receptacle spacing
- Appliances, motors, and transformers
- Generator requirements and battery storage systems
- Load calculations for motors and continuous loads
Special Occupancies – Articles 500 to 590
Special occupancies are situations where different safety rules apply due to the environment or use of space. You may see questions related to:
- Hazardous locations (Class I, II, III)
- Healthcare facilities
- Aircraft hangars and gas stations
- Mobile and manufactured homes
- Places of assembly like theaters or auditoriums
Special Equipment – Articles 600 to 695
These articles cover unique equipment types and how they must be installed. Examples include:
- Signs and outline lighting
- Elevators, cranes, and hoists
- X-ray equipment and electro-medical devices
- Fuel cells, wind turbines, and energy production systems
- Swimming pools, hot tubs, and fountains
Special Conditions – Articles 700 to 770
This section includes emergency systems and energy management. Common exam topics here include:
- Emergency and legally required standby systems
- Fire alarm circuits and communications wiring
- Energy storage and energy management systems
- Limited energy installations and intersystem bonding
Communications Systems – Articles 800 to 840
Though fewer questions appear from this section, it’s still worth reviewing. You may see questions about:
- Telephone and data cabling systems
- CATV and satellite distribution
- Antennas, radio, and television systems
- Network equipment and grounding
What Types of Questions Are on the NEC Portion?
While the NEC portion makes up the majority of the journeyman electrician test, most questions fall into two categories: code lookup and code calculation questions. Understanding the difference between the two is key to your success.
Code Lookup Questions
These questions are all about knowing how to navigate the NEC book. You’ll be asked about very specific rules or exceptions—things you likely won’t memorize. For example, the question might ask about burial depth for a specific type of conduit given the location, or the minimum clearance around electrical panels in a commercial setting.
The goal is to quickly locate the correct article and subsection in the NEC to answer the question confidently.
Examples:


Answer Key (Click to Expand)
Question 1: A – terminal and junction
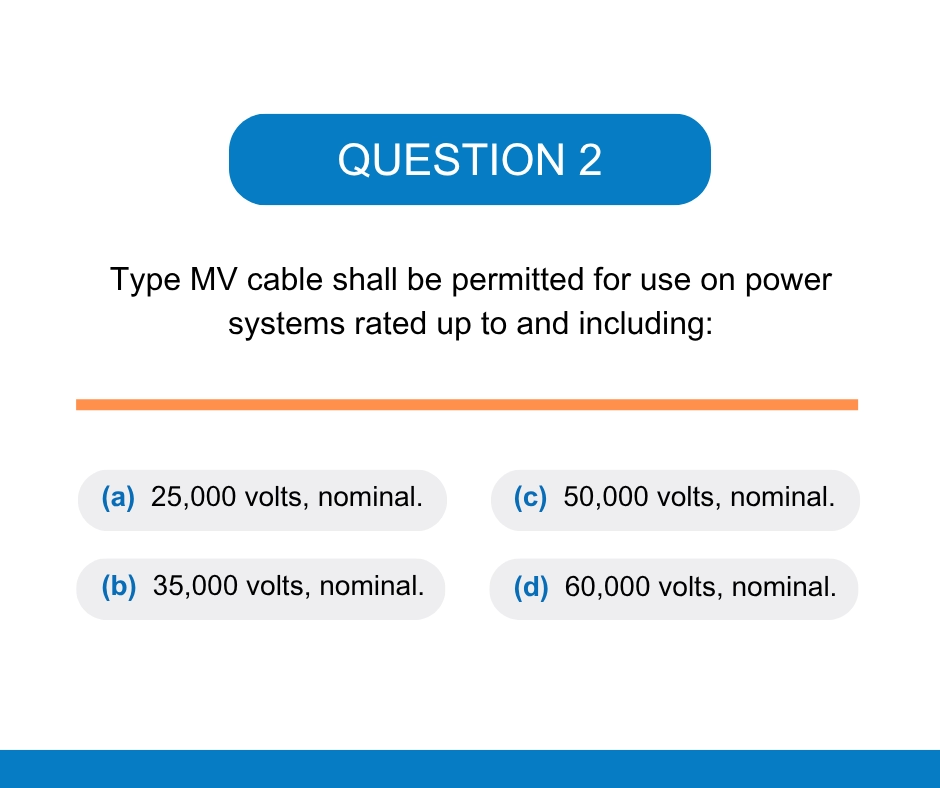
Question 2: B – 35,000 volts, nominal
Question 3: D – 300
Code Calculation Questions
Code calculation questions require more than just finding a code reference—they involve interpreting information and following a multi-step process to arrive at the correct answer. You’ll still need to know where to look in the NEC, but you’ll also need to understand how to apply it.
Here are some of the most common types of code calculations you might see:
- Conductor sizing
- Feeder and service load calculations for dwellings and commercial buildings
- Optional method service and feeder loads
- Grounding conductor and bonding calculations
- Conductor ampacity adjustment and correction
- Box fill calculations
- Pull box sizing
- Motor overload and overcurrent protection sizing
- Motor circuit and feeder conductor sizing
- Transformer protection requirements
Examples:


Answer Key (Click to Expand)
Question 1: D – 6 AWG
Question 2: B – 8 AWG
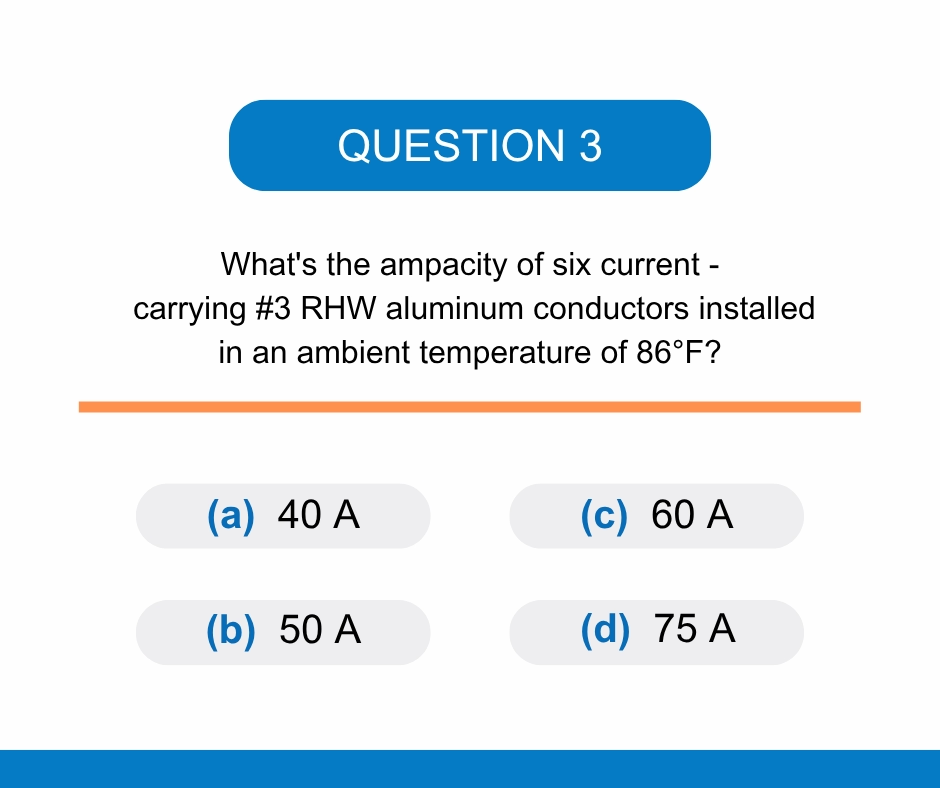
Question 3: C – 60 A
Try Out These Problems and More!
Get instant access to a 100% free, timed journeyman electrician practice exam – built to match the real test and covering all the major topics.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Versions, Explained
One of the most confusing parts about preparing for the journeyman electrician exam is figuring out which version of the National Electrical Code (NEC) your state is actually testing you on.
The NEC is updated every three years—but states don’t all switch over at the same time. Some states are quick to adopt the latest edition, while others may be years behind, still using the 2017 or even the 2014 code.
To make things more confusing, some states adopt the latest NEC version into their building codes, but the exam is still based on an older edition. That’s why it’s critical to study based on the version your exam is testing on, not just what’s used in the field.
We’ve included a helpful reference map below that shows the NEC version currently used for testing in each state. Be sure to check before you start studying, and always base your prep on the official exam bulletin for your state.

Electrical Theory Questions
While the NEC makes up the bulk of the journeyman electrician exam, many states also include a small portion of questions on basic electrical theory. These questions are usually straightforward but require a solid understanding of core principles.
They’re designed to test your ability to apply real-world concepts like voltage, current, resistance, and power.
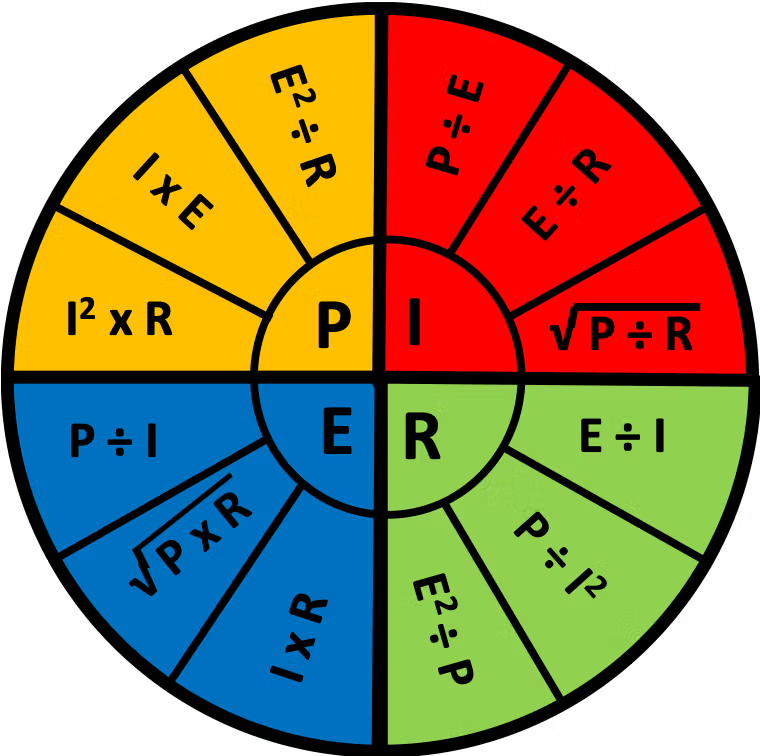
You won’t need to memorize complex formulas, but you should be comfortable with simple calculations and the relationships between electrical values.
Common theory topics may include:
- Ohm’s Law (E = I × R)
- Series and parallel circuits
- Power and energy calculations (Watts, VA, kWh)
- AC vs. DC current
- Voltage drop
- Power factor and efficiency
- Transformer basics
- Electrical units and conversions
Journeyman Electrician Exam Format
The journeyman electrician exam is always a timed, proctored test taken at an approved testing center on a computer. You can’t take it from home or online.
Most states structure the exam with around 100 multiple choice questions, giving you three to four hours to complete it. The test is open book, but the way you’re allowed to use the NEC codebook can vary widely.

In some states, you’re allowed to bring your own codebook into the exam – often with tabs and handwritten notes to help you navigate faster. In others, you’ll be given a plain, unmarked copy of the NEC that you must use during the test. Knowing which version of the NEC your state uses and how to navigate it efficiently is critical.
You’ll also receive scratch paper and a pen or pencil to work out calculations. Some testing centers allow a basic calculator, but not all. If in doubt, call your testing provider ahead of time to clarify what’s allowed.
Mastering the structure of the exam and the tools available to you can make a major difference on test day.
How the Journeyman Exam Is Scored

To pass the journeyman electrician exam, most states require a minimum score of 70%. That means you need to answer at least 70 out of 100 questions correctly to earn a passing grade.
You’ll typically receive your results immediately after finishing the test. If you pass, the system will simply tell you that you passed—you likely won’t see your exact score. However, if you don’t pass, you’ll usually receive your score along with a topic breakdown showing which areas you struggled with. This can be incredibly helpful in preparing for your retake.
Keep in mind that retake rules and waiting periods vary by state, so make sure to check with your licensing board if that applies to you.

Take Our Free Journeyman Electrician Practice Test
100% Free Timed Journeyman Electrician Practice Exam!
No Credit Card or Trial Required.
How to Prepare for the Journeyman Electrician Exam
Over half of first-time test takers fail the journeyman electrician exam. That statistic alone should tell you one thing — this test is not easy, and underestimating it is a mistake.
It’s not just about being a good electrician. It’s about knowing how to navigate the codebook, solve complex calculations, and answer questions under time pressure.

If you want to give yourself the best chance at passing, the smartest move is to take a prep course. A full prep course will walk you through everything you need — including NEC navigation techniques, code-based calculations, theory refreshers, and gradually structured lessons to build your confidence. It should also include timed simulation exams so you can practice under real test conditions.
In fact, we offer one ourselves.

Pass Your Journeyman Exam or Your Money Back!
Enrollment in our premium journeyman prep course gets you a full years worth of access to all of our materials, plus a Pass the Exam Money Back Guarantee!
Select Your State and Click the Button to Learn More!
Beyond the lessons, the single most important step in your preparation is taking practice exams. If you don’t take practice exams, you won’t know what to expect — and you’ll have no real way to measure how ready you are. Practicing with realistic, timed exams not only builds confidence, it helps you identify the areas where you still need work.
Strategies for Test Day
The journeyman electrician exam isn’t just a test of what you know — it’s a test of how well you perform under pressure. With around 100 questions and only 3 to 4 hours to complete them, time management is one of the biggest challenges. Here are some key strategies to help you stay focused and in control on exam day:
- Arrive early and prepared. Bring valid ID and your NEC codebook (if your state allows it). Review the rules ahead of time so there are no surprises.
- Use your NEC efficiently. Practice flipping to key articles and tables during your study sessions so it becomes second nature on test day.
- Skip and return. Don’t get stuck on one question. If you’re unsure, flag it and move on — come back after you’ve answered the ones you know.
- Stay calm under pressure. Trust your preparation and don’t panic if you hit a tough section. Most test centers offer scratch paper to help you stay organized during calculations.
- Memorize key NEC tables. One of the best ways to save time is to know exactly where the most-used calculation tables are. If you don’t have to spend time flipping through the index, you’ll be able to complete more questions confidently and avoid rushing at the end.

Even experienced electricians can fail the journeyman exam — not because they don’t know the material, but because they weren’t prepared for the format, pace, or structure of the test. Here are some of the most common mistakes that hold people back:
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Studying the Wrong NEC Code Year Make sure you're using the correct version of the NEC for your state. Studying from the wrong edition can cause confusion and lead to incorrect answers on test day.
- Trying to Memorize Instead of Using the Codebook The exam is open book for a reason. Focus on learning how to navigate the NEC efficiently instead of trying to memorize exact code sections.
- Skipping Code-Based Calculations Avoiding math and calculation questions during prep will hurt you on test day. These show up often, and practicing them can save you time and points.
- Bringing the Wrong Codebook to the Testing Center Some states only allow clean, unmarked NEC books. If yours has tabs or notes and your state doesn’t allow them, you could be turned away.
- Letting Stress or Time Pressure Take Over Anxiety and poor time management can throw off your performance. Practicing under timed conditions helps you stay calm and focused when it counts.

Take Our Free Journeyman Electrician Practice Test
100% Free Timed Journeyman Electrician Practice Exam!
No Credit Card or Trial Required.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who administers the Journeyman Electrician Exam?
The exam is typically administered by national testing providers like PSI, Pearson VUE, or PROV, depending on your state. These companies are contracted by state licensing boards to manage scheduling, proctoring, and grading. Your state’s licensing board will direct you to the correct testing agency when you apply.
How many questions are on the Journeyman Electrician Exam?
Most states include around 80 to 100 multiple choice questions, and the test usually takes 3 to 4 hours to complete. The number can vary depending on the state, but the format is always open-book and NEC-based.
What score do I need to pass the exam?
A score of 70% or higher is typically required to pass. You’ll usually receive your results immediately after finishing. If you don’t pass, some testing providers will also include a category breakdown to help you identify weak areas.
Where can I find a free practice exam?
We offer a 100% free Journeyman Electrician practice test, designed to simulate the real exam format and difficulty. You can select your state and get started here — no payment or commitment required.
What version of the NEC is the exam based on?
That depends on your state. The National Electrical Code (NEC) is updated every three years, but many states take time to adopt the latest version. Always check your state’s official licensing board or testing provider to confirm which NEC year your exam will be based on.
What topics are covered on the exam?
The exam primarily tests your knowledge of the NEC, including topics like wiring methods, grounding and bonding, box and conductor sizing, and special occupancies. Some states also include a portion on electrical theory, safety, and math-based calculations.
Can I bring my own codebook to the journeyman electrician exam?
Some states allow you to bring your own NEC book with tabs and handwritten notes, while others require a clean, unmarked version that they provide at the testing center. Check with your testing agency in advance so you’re not caught off guard.
Is the exam really open book?
Yes! Every version of the Journeyman Electrician Exam is open book, and you’ll be allowed to reference the NEC throughout the test. But don’t rely on the codebook alone — you still need to know how to navigate it quickly and apply the rules correctly under timed conditions.
How many times can I retake the exam if I fail?
Most states allow multiple retakes, though you may need to wait a set number of days between attempts and pay a retesting fee. Some states also cap the number of attempts before requiring a re-application, so it’s best to check your state’s rules.
How do I pass the Journeyman Electrician Exam?
The best way to pass is to study the National Electrical Code (NEC) thoroughly and take realistic practice exams. Use a prep course to guide your learning, especially for code lookups, calculations, and navigating the codebook quickly under pressure. Make sure you’re using the correct NEC version for your state.
How much is the Journeyman Electrician Test?
The cost varies by state but typically ranges from $75 to $150 per attempt. The fee is paid directly to the testing provider—like PSI, Pearson VUE, or PROV—when you schedule your exam. Check your state’s licensing board for the most accurate fee details.
